
Recent industry surveys show that carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel dominate bolt selection in Rail Components for Construction Equipment. Alloy steel bolts deliver strength and environmental resistance. Manufacturers choose these materials to handle heavy stress and harsh environments, ensuring performance, durability, and safety remain top priorities.
Key Takeaways
- Choosing the right bolt material—carbon steel, alloy steel, or stainless steel—directly affects the strength, durability, and safety of rail components in construction equipment.
- Proper bolt material selection and protective coatings reduce corrosion and fatigue failures, extending service life and lowering maintenance costs.
- Engineers should balance performance needs, environmental conditions, and cost while following industry standards to ensure reliable and safe bolt use in demanding construction environments.
Importance of Bolt Material Selection in Rail Components for Construction Equipment

Impact on Rail Performance
Bolt material selection plays a vital role in the mechanical performance of rail components for construction equipment. The chosen material affects several key properties:
- Strength under heavy loads
- Resistance to corrosion in harsh environments
- Fatigue resistance during repeated use
- Overall durability and service life
Carbon steel bolts offer strength and cost-effectiveness, but they often need protective coatings to prevent rust. Stainless steel bolts provide excellent corrosion resistance, making them suitable for environments with moisture or chemicals. Alloy steel bolts deliver enhanced strength and fatigue resistance, which is essential for demanding structural applications. These material choices directly influence how well rail components perform in the field.
Safety Considerations
Safety remains a top priority in construction equipment. The right bolt material helps prevent unexpected failures that could lead to accidents or equipment damage. For example, a study on 60Si2Mn steel bolts used in rail fastenings showed fatigue failure after eight years, even though the bolts had proper hardness and surface treatment. This finding highlights that material selection must consider not only strength but also fatigue resistance and long-term reliability. Engineers must evaluate both the environment and the expected loads to ensure safe operation.
Longevity and Maintenance
The longevity of rail components for construction equipment depends on the bolts’ ability to withstand wear, corrosion, and fatigue. Stainless steel bolts reduce the need for frequent maintenance in corrosive settings. Alloy steels extend service life by resisting fatigue and dynamic loading. Choosing the right material minimizes downtime and maintenance costs, supporting efficient and reliable equipment operation.
Common Bolt Materials for Rail Components for Construction Equipment
Carbon Steel Grades
Carbon steel bolts remain a staple in the assembly of rail components for construction equipment. Manufacturers often select medium carbon steel for its balance of strength, hardness, and cost-effectiveness. Medium carbon steel, with a carbon content ranging from 0.25% to 0.60%, can be heat treated to improve toughness and wear resistance. ASTM A572 Grade 50, for example, delivers a tensile strength of approximately 65,000 psi (about 450 MPa), making it suitable for heavy-load structural applications.
| Grade/Class | Material Type | Proof Strength (MPa) | Minimum Yield Strength (MPa) | Minimum Tensile Strength (MPa) | Core Hardness (Rockwell) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.8 | Low to medium carbon steel | 310 | 340 | 420 | B71 – 95 |
Grade 4.8 bolts, made from low to medium carbon steel, offer high strength for demanding applications. Higher grades, such as 8.8 and above, use heat-treated medium-carbon or low-carbon alloy steel to achieve even greater strength and hardness. Ningbo Digtech (YH) Machinery Co.,Ltd. supplies a wide range of carbon steel bolts, ensuring reliable performance for critical rail connections.
Tip: Carbon steel bolts often require protective coatings to prevent rust, especially in outdoor or humid environments.
Alloy Steels
Alloy steel bolts provide enhanced mechanical properties by incorporating elements such as chromium, molybdenum, and nickel. These bolts deliver improved strength and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty rail components in construction equipment. SAE J429 Grade 8 and ASTM A193 Grade B7 represent common choices for high-strength applications.
- Alloy steel bolts withstand harsh weather conditions, reducing the risk of rust or moisture damage.
- They offer easier weldability compared to some carbon steels, which benefits fabrication and assembly.
- Their superior fatigue resistance extends the service life of rail components under dynamic loads.
However, alloy steel bolts come with higher costs and reduced malleability, which can limit shaping or forming during manufacturing. Processing challenges may arise due to the presence of alloying elements. While alloy steel offers better corrosion resistance than standard carbon steel, it still requires protective treatments in aggressive environments.
Ningbo Digtech (YH) Machinery Co.,Ltd. provides alloy steel bolts engineered for resilience and reliability, supporting the demanding needs of modern construction equipment.
Stainless Steels
Stainless steel bolts stand out for their exceptional corrosion resistance and durability. Industries that require long-lasting, low-maintenance fasteners often choose stainless steel for rail components in construction equipment. Austenitic grades such as 304 and 316 resist rust and corrosion, even in harsh or outdoor environments.
- Stainless steel bolts require minimal maintenance and do not need special coatings.
- They maintain integrity across a wide range of temperatures.
- Their long product life reduces replacement frequency and downtime.
Despite these advantages, stainless steel bolts typically cost more than carbon steel alternatives. Fabrication can be more complex, and in saltwater environments, certain stainless grades may still face corrosion challenges. Compatibility with other metals is crucial to prevent galvanic corrosion.
Ningbo Digtech (YH) Machinery Co.,Ltd. offers a comprehensive selection of stainless steel bolts, ensuring optimal performance and longevity for rail components exposed to demanding conditions.
Specialty Materials and Coatings (e.g., Zinc-Coated Bolts, Duplex Stainless Steels, Hot-Dip Galvanized Finishes)
Specialty materials and advanced coatings further enhance the durability and performance of bolts in rail components for construction equipment. Protective coatings such as Greenkote and Zn-Ni provide exceptional corrosion resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 600°C and salt spray exposure for up to 1,200 hours. These coatings maintain thread integrity and avoid hydrogen embrittlement, making them suitable for critical applications.
| Coating Type | Key Properties and Benefits | Suitability for Bolts in Rail/Construction Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Phosphating | Good torque-preload consistency; avoids hydrogen embrittlement; suitable for high-strength bolts (grade 10.9+); temperature range 107~204°C; requires oiling for corrosion resistance | Often used for important connection parts; enhances durability and thread integrity |
| Electric Galvanizing | Low cost; good appearance; limited corrosion resistance; risk of hydrogen embrittlement; poor torque-preload consistency; generally not used for bolts above grade 10.9 | Less suitable for critical bolts due to embrittlement and inconsistent preload |
| Zn-Ni Coatings | Superior corrosion resistance; wear resistance; heat tolerance; extends life in harsh environments; suitable for critical fasteners exposed to weather and stress | Highly effective for bolts in rail and construction equipment exposed to harsh conditions |
| Greenkote Coatings | High corrosion protection up to 600°C; salt spray resistance up to 1,200 hours; no hydrogen embrittlement; approved by major international standards; maintains thread integrity | Widely used in construction and rail industries; suitable for demanding applications |
Duplex stainless steels combine high strength with excellent corrosion resistance, making them suitable for the most challenging environments. Hot-dip galvanized finishes offer a cost-effective way to protect carbon steel bolts from rust and wear.
Ningbo Digtech (YH) Machinery Co.,Ltd. integrates these specialty materials and coatings into its product line, helping clients achieve maximum bolt durability and performance in every application.
Comparative Analysis of Bolt Materials in Rail Components for Construction Equipment
Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
Strength and load-bearing capacity define the suitability of bolt materials for demanding applications. Alloy steel bolts, especially those classified as high tensile steel, deliver the highest strength among commonly used fasteners. Grade 12.9 bolts, produced from quenched and tempered alloy steel, withstand extreme stress and strain, making them ideal for critical connections in construction equipment.
The following table compares the tensile strength ranges of different bolt materials:
| Steel Type | Tensile Strength Range (MPa) |
|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | 325 to 924 (varies by carbon content) |
| Stainless Steel | 450 (ferritic) to 660 (martensitic) |
| Alloy Steel | Up to 960 (Grade 12.9 and similar) |
Alloy steel bolts, with tensile strengths reaching up to 960 MPa, outperform carbon steel bolts, which range from 325 to 924 MPa depending on their carbon content. Stainless steel bolts offer moderate strength, with values between 450 and 660 MPa. High tensile steel bolts, often made from alloy steel, are the preferred choice for applications where maximum load-bearing capacity is essential. Ningbo Digtech (YH) Machinery Co.,Ltd. supplies a comprehensive range of high-strength bolts, ensuring reliable performance in the most demanding rail component assemblies.
Fatigue Resistance
Fatigue resistance measures a bolt’s ability to withstand repeated loading and unloading cycles without failure. In rail components for construction equipment, bolts experience significant cyclic stresses due to vibration and dynamic loads. Alloy steel bolts provide superior fatigue strength because of their toughness and heat-treatable properties. Stainless steel bolts also perform well, especially in corrosive environments, while carbon steel bolts offer good fatigue resistance if properly treated and coated.
| Material Type | Key Properties | Fatigue Resistance Performance | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy Steel | High tensile strength, excellent toughness, heat-treatable | Superior fatigue strength due to strength and toughness | Heavy machinery, structural bolts |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistant, moderate to high strength, some heat-treatable grades | Good fatigue resistance, especially in corrosive environments | Marine, chemical plants |
| Carbon Steel | High to moderate strength, widely available | Good fatigue resistance if properly treated and coated | General construction and engineering |
Experimental studies show that fatigue wear is the main failure mechanism in bolted structures under cyclic loading. Increased loading amplitude accelerates thread damage and loosening, leading to fatigue fractures. Surface treatments such as shot peening and rolled threads can improve fatigue life by inducing beneficial compressive stresses.
The fatigue life of Q235 steel bolts, commonly used in fasteners, decreases sharply as installation torque increases. The following chart illustrates this relationship:
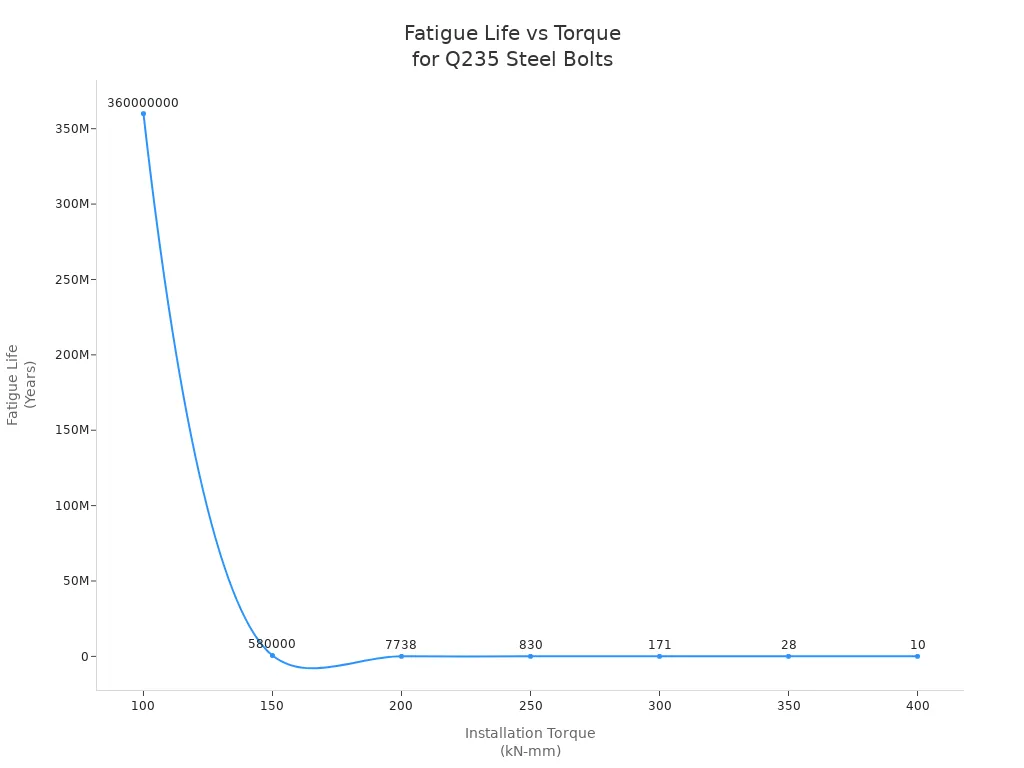
Proper installation and surface treatment play a crucial role in maximizing fatigue resistance. Ningbo Digtech (YH) Machinery Co.,Ltd. offers bolts with advanced surface treatments and precise manufacturing, supporting extended fatigue life in rail applications.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance ensures the longevity and reliability of bolts exposed to harsh construction environments. Stainless steel bolts provide the best corrosion resistance, making them suitable for environments with high moisture or chemical exposure. Alloy steel bolts offer moderate corrosion resistance, especially when coated or treated. Carbon steel bolts require protective coatings, such as hot-dip galvanizing, to prevent rust and degradation.
| ISO Category | Typical Environment Description | Corrosivity Level | Corrosion Rate for Zinc Coating (µm/year) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | Desert, dry/cold, very low pollution | Very Low | < 0.1 |
| C2 | Rural, temperate, low pollution | Low | 0.1 – 0.7 |
| C3 | Urban, medium pollution | Medium | 0.7 – 2.1 |
| C4 | Industrial, high pollution | High | 2.1 – 4.2 |
| C5 | Marine, very high pollution | Very High | 4.2 – 8.4 |
| CX | Offshore, extreme pollution | Extreme | 8.4 – 25 |
Steel bolts face several corrosion mechanisms, including stress corrosion cracking, hydrogen embrittlement, and galvanic corrosion. Protective coatings, such as hot-dip galvanizing or epoxy, help mitigate these risks. Stainless steel and duplex-coated bolts are recommended for aggressive environments. Ningbo Digtech (YH) Machinery Co.,Ltd. provides a variety of corrosion-resistant bolt options, ensuring optimal performance in diverse construction site conditions.
Tip: Selecting the right bolt material and coating based on the environment can significantly extend the service life of rail components for construction equipment.
Cost and Availability
Cost and availability influence material selection for rail components. Ordinary carbon steel bolts are the most affordable and widely available, making them a popular choice for general construction. Alloy steel bolts, which undergo specialized heat treatment and surface finishing, cost more than standard carbon steel bolts but offer higher strength and durability. Stainless steel bolts have the highest initial cost due to their corrosion resistance and finishing requirements.
Mild steel bolts remain less expensive than stainless steel bolts, which require additional processing. Despite the higher price, stainless steel bolts provide long-term value in environments where corrosion is a concern.
ASTM A325 and A490 bolts, including stainless steel variants, are globally available through suppliers like Ningbo Digtech (YH) Machinery Co.,Ltd. These bolts come in various types and sizes, supporting a wide range of applications from structural steel to heavy machinery. Suppliers maintain extensive inventories and offer custom manufacturing, ensuring fast delivery and reliable supply for construction projects worldwide.
Methods for Bolt Material Analysis in Rail Components for Construction Equipment
Laboratory Testing (Tensile, Hardness, Fatigue)
Laboratory testing forms the foundation for evaluating bolt materials. Engineers use a range of mechanical and chemical tests to ensure bolts meet performance standards. The following table summarizes common laboratory testing methods:
| Testing Method | Description and Purpose |
|---|---|
| Tensile Testing | Measures material strength by pulling the bolt until failure, assessing ultimate tensile strength. |
| Proof Load Testing | Verifies bolt strength under specified loads to ensure compliance with standards. |
| Shear Testing | Assesses the bolt’s ability to resist shear forces, critical for joint integrity. |
| Wedge Testing | Evaluates head soundness and mechanical integrity of bolt heads. |
| Hardness Testing | Determines resistance to indentation and wear using Rockwell, Brinell, or Vickers methods. |
| Fatigue Testing | Determines durability under cyclic loading, predicting lifespan under repeated stress. |
| Prevailing Torque Testing | Measures resistance to loosening under vibration or stress. |
| Metallurgical Analysis | Examines internal structure and quality, including microhardness and decarburization. |
| Chemical Analysis | Verifies material composition and compliance using advanced spectroscopy. |
| Environmental Testing | Assesses coating and corrosion resistance through salt spray and humidity exposure. |
Non-destructive testing, such as ultrasonic and magnetic particle methods, detects internal flaws without damaging the bolts. Destructive tests, including tensile and fatigue testing, provide critical data on strength and durability.
Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) allows engineers to simulate bolt performance under real-world conditions. They create detailed models of bolt connections to analyze stress distributions and predict failure points. FEA evaluates fatigue life and failure modes under complex loading, such as combined transverse and axial forces. Simulations incorporate mechanical properties and preload conditions, offering insight into how different materials behave under operational loads. This approach helps engineers compare bolt materials and optimize designs for durability and safety.
- FEA models replicate operational stresses and validate theoretical predictions.
- Numerical simulations assess fatigue life and identify potential failure modes, such as loosening or fracture.
- Engineers use FEA results to refine material selection and improve bolt reliability.
Field Performance Data
Field performance data provides real-world validation for laboratory and simulation results. Engineers collect data from bolts in service, monitoring for signs of wear, fatigue, or corrosion. They analyze failure rates, maintenance records, and environmental exposure to assess long-term performance. Field data highlights issues that may not appear in controlled tests, such as unexpected loading patterns or environmental factors. This feedback loop ensures continuous improvement in bolt material selection and design.
Note: Combining laboratory testing, FEA, and field data gives a comprehensive understanding of bolt performance, supporting safer and more reliable construction equipment.
Common Failure Modes and Material Mitigation in Rail Components for Construction Equipment
Fatigue Cracking
Fatigue cracking stands as the most frequent failure mode in bolts. Repeated loading and unloading cycles cause microscopic cracks to form at stress concentrations, such as thread roots or surface imperfections. Over time, these cracks grow and eventually lead to sudden fracture. Insufficient preload often accelerates fatigue by allowing joint movement, which increases stress on the bolt. Poor installation, such as improper tightening or mismatched hardware, also contributes to fatigue failure. To mitigate this risk, engineers recommend using threadlocking adhesives, mechanical locking devices, and routine inspections. These measures help maintain preload and prevent vibration-induced loosening.
Corrosion and Environmental Degradation
Corrosion significantly reduces bolt lifespan, especially in environments with high humidity, temperature fluctuations, or airborne pollutants. Moisture, particularly water vapor and condensation, initiates electrochemical reactions that degrade metal surfaces. Pollutants like sulfur dioxide and solid particles lower the humidity threshold for corrosion, making bolts vulnerable even at moderate moisture levels. Specific corrosion types—such as galvanic, pitting, and crevice corrosion—occur when bolts contact dissimilar metals or trap moisture in confined spaces. Preventive strategies include selecting corrosion-resistant materials, applying protective coatings, and controlling environmental exposure through design and maintenance.
Shear and Tensile Failures
Shear and tensile failures occur when bolts experience forces that exceed their mechanical limits. High-strength bolts, produced from carbon or alloy steels and fully heat-treated, resist these failures by achieving superior tensile and shear strength. Heat treatment processes like quenching and tempering develop a tough, tempered martensitic microstructure. This structure, combined with refined grain size and controlled alloy content, enhances both strength and toughness. Proper material selection, precise heat treatment, and attention to installation torque help prevent premature failure under heavy loads.
Recommendations for Bolt Material Selection in Rail Components for Construction Equipment
Application-Specific Guidelines
Selecting the right bolt material depends on the specific application and operational environment. Engineers must match material properties to the demands of each use case. The following table summarizes key guidelines for material selection:
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High corrosion resistance; ideal for outdoor and marine environments | Higher cost compared to carbon steel |
| Carbon Steel | Strong, durable, and cost-effective | Requires protective coatings to prevent rust |
| Titanium | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio; suitable for extreme environments | Expensive and less commonly used |
Stainless steel bolts work best in environments with high humidity, outdoor exposure, or marine conditions. Carbon steel bolts suit general construction where strength and cost matter most, but they need coatings like galvanization or zinc plating for protection. Titanium and alloy steels serve well in high-strength or extreme environments.
Environmental factors such as humidity, temperature, and chemical exposure influence material choice. Protective coatings extend bolt life in harsh conditions. Engineers should avoid mismatched materials, such as pairing stainless steel bolts with carbon steel nuts, to prevent galvanic corrosion. Meeting or exceeding load requirements ensures safety and durability. Regular inspection and maintenance help detect early signs of wear or corrosion.
The table below links bolt grades to their recommended applications:
| Grade | Material Type | Typical Applications and Environments |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM A307 | Low- to medium-strength carbon steel | Non-critical joints, light wood framing, HVAC, electrical enclosures |
| ASTM A325 | High-strength structural steel | Structural steel connections, beams, columns, trusses |
| ASTM A354 BD | Alloy steel | Load-bearing beams, bridges, infrastructure requiring high strength |
| Metric 8.8 | High-tensile steel | Automotive, machinery, bridges |
| Metric 10.9 | Higher tensile strength steel | Heavy machinery, construction & mining equipment |
| Metric 12.9 | Very high tensile strength steel | Aviation, offshore drilling, oil & gas applications |
| Stainless Steel A2 | Stainless steel | Food processing, moderate corrosion environments |
| Stainless Steel A4 | Stainless steel | Marine environments, saltwater exposure |
ASTM and ISO standards guide the selection of bolt grades based on strength and environmental needs. High-strength grades like 10.9 and 12.9 are common in heavy-duty and extreme environments.
Balancing Performance and Cost
Engineers must balance performance requirements with cost when selecting bolt materials for rail components. The following points outline a practical approach:
- Evaluate load requirements, including tensile, shear, and fatigue stresses, to select bolts with adequate strength.
- Consider environmental conditions such as moisture, chemicals, saltwater, UV exposure, and temperature extremes. Choose corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel or coated steel for harsh environments.
- Ensure compliance with regulatory standards (ASTM, ISO, DIN, SAE) for quality and traceability.
- Factor in installation and maintenance needs, including ease of removal and tool accessibility.
- Look beyond initial purchase price. Assess lifecycle value by considering durability, maintenance frequency, and replacement costs.
- Use common materials such as various grades of steel for general applications, stainless steel for corrosion resistance, and alloy steels for high-stress situations.
- Partner with reputable suppliers who provide certified products and technical support.
This approach helps engineers achieve reliable performance and cost efficiency for Rail Components for Construction Equipment. By considering both upfront and long-term factors, teams can optimize safety, durability, and budget.
Tip: Always review the total cost of ownership, not just the initial material cost. Long-lasting bolts may reduce maintenance and replacement expenses over time.
Industry Standards and Best Practices
Industry standards ensure that bolt materials meet strict requirements for safety and performance. The following table lists key standards relevant to rail components in construction equipment:
| Standard Identifier | Scope and Application |
|---|---|
| ISO 6305-4:1985 | Technical delivery requirements for untreated steel nuts and bolts, and high-strength bolts for railway fastenings |
| ASTM A193/A193M-24a | Alloy-steel and stainless steel bolting for high temperature, high pressure, and special purpose applications |
| ASTM A320/A320M-24a | Alloy-steel and stainless steel bolting for low-temperature service, suitable for cold environments |
| SAE J 1102-2016 | Mechanical and material requirements for wheel bolts in construction and rail equipment |
| SAE J 1102M-2016 | Metric wheel bolts, ensuring compatibility and performance in construction equipment |
| ASTM D4435-13e1 | Test methods for rock bolt anchor pull tests, relevant for bolted connections in construction |
| Additional ISO and ASME standards | Define bolt dimensions, grades, and types, supporting proper selection and testing by standardizing characteristics |
Engineers should always select bolts that comply with these standards. Adhering to recognized guidelines ensures quality, safety, and compatibility across projects. Best practices include verifying supplier certifications, conducting regular inspections, and maintaining detailed records of bolt specifications and performance.
Note: Following industry standards and best practices reduces the risk of failure and supports long-term reliability in demanding construction environments.
High-strength carbon steels, alloy steels, and stainless steels remain the top choices for bolts in Rail Components for Construction Equipment. Careful material analysis, including yield strength and non-destructive testing, supports safety and reliability. Engineers should select bolt materials based on operational loads, environmental exposure, and strict industry standards.
FAQ
What factors determine the best bolt material for rail components?
Engineers consider load requirements, environmental exposure, corrosion risk, and industry standards. Each factor influences material choice for optimal safety and durability.
How do coatings improve bolt performance in construction equipment?
Coatings protect bolts from corrosion and wear. They extend service life and reduce maintenance needs, especially in harsh or outdoor environments.
Can stainless steel bolts replace carbon steel in all applications?
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance. However, it may not provide the required strength or cost efficiency for every application. Material selection depends on specific project needs.
Tip: Always consult industry standards before selecting bolt materials for critical rail components.
Post time: Jul-20-2025