
Selecting the right hex bolt and nut is crucial for ensuring the longevity of construction equipment. Poor choices can lead to uneven thread load distribution, as highlighted by Motosh’s study, which identified softer nut materials as a contributing factor. Kazemi’s fatigue tests further revealed that multi-axial loading drastically reduces bolt lifespan, emphasizing the importance of material and design. High-quality fasteners, such as plow bolt and nut, track bolt and nut, or segment bolt and nut, prevent frequent failures, saving costs over time. Proper selection enhances durability, reduces maintenance, and maximizes performance in demanding environments.
Key Takeaways
- Picking the right material for bolts and nuts is important. Stainless steel resists rust well, while carbon steel is cheaper and strong.
- Knowing load limits is key for safety. Always pick fasteners that meet or go beyond the needed load for your construction work.
- Correct size and thread type make strong connections. Use size charts and tools like rulers to check measurements before using them.
- Buying good-quality fasteners saves money over time. Strong materials need less fixing and keep equipment working longer.
- Checking fasteners often helps avoid problems. Look for damage, rust, and proper load strength to keep your construction tools safe.
Material Selection for Hex Bolt and Nut

Common Materials and Their Properties
Choosing the right material for a hex bolt and nut is critical for ensuring durability and performance in construction applications. Each material offers unique properties that make it suitable for specific uses. Below is a comparison of commonly used materials:
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Excellent corrosion resistance; suitable for outdoor and marine applications | More expensive than regular steels |
| Carbon Steel | Strong and durable; cost-effective | May require coatings for rust protection |
| Titanium | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio; suitable for extreme environments | Higher cost; may not be widely used |
Stainless steel stands out for its corrosion resistance, making it ideal for outdoor and marine environments. Carbon steel, on the other hand, is a cost-effective option that provides strength and durability but often requires additional coatings to prevent rust. Titanium, though less common, offers an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for extreme conditions.
Understanding these properties helps in selecting the most appropriate material for a hex bolt and nut, ensuring the fasteners meet the demands of the construction environment.
Choosing Materials for Specific Environments
The environment in which a hex bolt and nut will be used significantly impacts material selection. For outdoor or marine applications, stainless steel is often the preferred choice due to its protective oxide layer that prevents oxidation and corrosion. This feature enhances its longevity and reduces maintenance costs over time.
In high-temperature or chemically aggressive environments, alloy steel with a black powder coating is highly effective. The coating not only improves corrosion resistance but also increases temperature resilience, making it suitable for demanding applications. For general construction purposes, carbon steel remains a popular choice due to its affordability and versatility, though it may require galvanization or zinc plating for added protection.
Tip: Always consider the environmental conditions, such as humidity, temperature, and exposure to chemicals, when selecting materials for hex bolts and nuts. This ensures the fasteners maintain their integrity and performance over time.
Benefits of Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, and Alloy Steel
Each material offers distinct advantages that cater to different construction needs:
- Stainless Steel: Known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, stainless steel accounts for over 30% of all fasteners used in construction. Its high strength-to-weight ratio allows for lighter structures, reducing material usage and environmental impact. Additionally, its durability leads to lower maintenance costs, making it a cost-effective choice in the long run.
- Carbon Steel: This material is widely used in construction due to its strength and affordability. It is ideal for applications where cost is a concern but strength cannot be compromised. With proper coatings, carbon steel fasteners can withstand harsh conditions, ensuring longevity.
- Alloy Steel: Offering enhanced mechanical properties, alloy steel is perfect for demanding applications. Its high tensile and yield strength make it suitable for heavy machinery and structural components. The design of long nuts in alloy steel fasteners reduces pressure on threads, increasing connection strength and stability.
By understanding the benefits of these materials, construction professionals can make informed decisions that enhance the performance and longevity of their equipment.
Evaluating Strength and Load Capacity
Understanding Load Ratings
Load ratings determine the maximum force a hex bolt and nut can withstand without failure. These ratings are essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of construction equipment. Engineers calculate load ratings based on factors such as material strength, bolt size, and thread design. For heavy construction applications, fasteners must meet specific proof load and hardness requirements to handle extreme stress.
The table below highlights the proof load and hardness data for various grades and styles of hex bolts and nuts:
| Grade | Style | Size (in.) | Proof Load (ksi) | Hardness (HBN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Hex | 1/4 – 1-1/2 | 90 | 68 |
| Heavy Hex | 1/4 – 4 | 100 | 75 | |
| B | Heavy Hex | 1/4 – 1 | 133 | 100 |
| Heavy Hex | 1-1/8 – 1-1/2 | 116 | 87 |
Note: Heavy hex nuts are thicker than standard hex nuts, providing higher proof load strength as per ASTM A563 standards.
Understanding these ratings helps construction professionals select fasteners that align with the mechanical demands of their equipment, ensuring durability and safety.
Industry Standards for High-Strength Fasteners
Industry standards play a critical role in defining the performance and reliability of high-strength fasteners. These standards ensure consistency in manufacturing and provide benchmarks for evaluating tensile strength, hardness, and durability. Below are some key standards for hex bolts and nuts used in construction:
| Standard | Description | Minimum Tensile Strength |
|---|---|---|
| A354-17e2 | Quenched and Tempered Alloy Steel Bolts, Studs, and Fasteners | N/A |
| F2882/F2882M-17 | Alloy Steel Screws, Heat Treated | 170 ksi / 1170 MPa |
| F3125/F3125M-25 | High Strength Structural Bolts and Assemblies | 120 ksi, 144 ksi, 150 ksi / 830 MPa, 1040 MPa |
| F3043-23 | Twist Off Type Tension Control Structural Bolt Assemblies | 200 ksi |
| F3111-23 | Heavy Hex Structural Bolt/Nut/Washer Assemblies | 200 ksi |
| F3148-17a(2024) | High Strength Structural Bolt Assemblies | 144 ksi |
These standards, such as ASTM F3125 and F3043, ensure that fasteners meet the mechanical requirements for heavy-duty applications. Construction professionals should always verify compliance with these standards when selecting fasteners for critical projects.
Applications Requiring High-Strength Hex Bolts and Nuts
High-strength hex bolts and nuts are indispensable in applications where heavy loads and extreme conditions are present. These fasteners are commonly used in:
- Structural Steel Connections: High-strength bolts secure beams and columns in buildings and bridges, ensuring stability under dynamic loads.
- Heavy Machinery: Equipment such as excavators and cranes rely on durable fasteners to handle operational stress and vibrations.
- Industrial Plants: Facilities with high-temperature or corrosive environments require fasteners made from alloy steel or stainless steel for enhanced performance.
- Marine Construction: Stainless steel fasteners resist corrosion in saltwater environments, making them ideal for docks and offshore platforms.
The chart below illustrates the relationship between proof load and hardness for various bolt grades, emphasizing the importance of selecting the right fastener for specific applications:
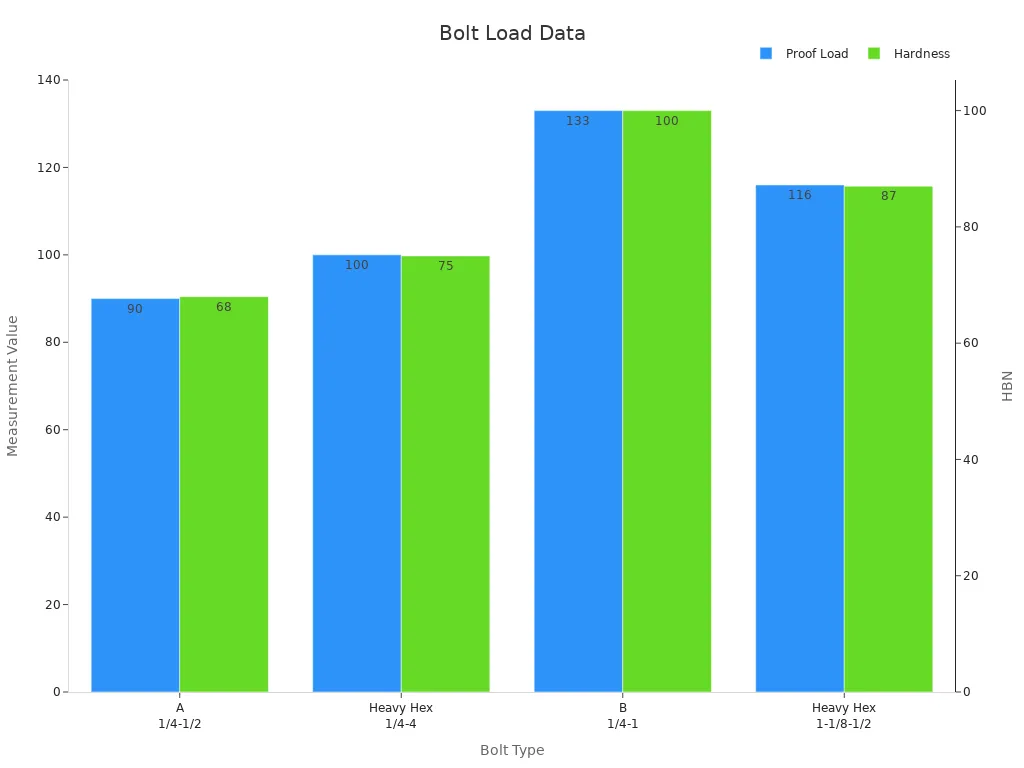
Selecting the appropriate hex bolt and nut for these applications ensures the longevity and safety of construction equipment. Professionals must consider load ratings, industry standards, and environmental factors to make informed decisions.
Size and Thread Specifications
Selecting the Correct Size for Construction Equipment
Choosing the correct size of a hex bolt and nut is essential for ensuring a secure and reliable connection in construction equipment. The size directly impacts the fastener’s ability to handle loads and maintain structural integrity. Dimensional charts and tolerance data provide valuable guidance for selecting the appropriate size. The table below outlines key dimensions for hex fasteners:
| Bolt Diameter | Body Diameter | Width Across Flats | Width Across Corners | Height | Thread Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2 | 0.515 | 7/8 | 0.875 | 1.010 | 5/16 |
| 5/8 | 0.642 | 11/16 | 1.062 | 1.227 | 25/64 |
| 3/4 | 0.768 | 11/4 | 1.250 | 1.443 | 15/32 |
| 7/8 | 0.895 | 17/16 | 1.438 | 1.660 | 35/64 |
| 1 | 1.022 | 15/8 | 1.625 | 1.876 | 39/64 |
Tip: Always refer to dimensional charts to ensure the selected fastener matches the equipment’s requirements.
Thread Pitch and Fit Considerations
Thread pitch and fit play a critical role in the compatibility of hex bolts and nuts. Thread pitch refers to the distance between threads, while fit determines how tightly the bolt and nut engage. A mismatch in thread pitch can lead to improper fastening, reducing the connection’s strength. For construction equipment, coarse threads are often preferred due to their higher resistance to stripping and ease of assembly.
The chart below illustrates the relationship between bolt diameter and thread dimensions, helping professionals select the right fit for their applications:
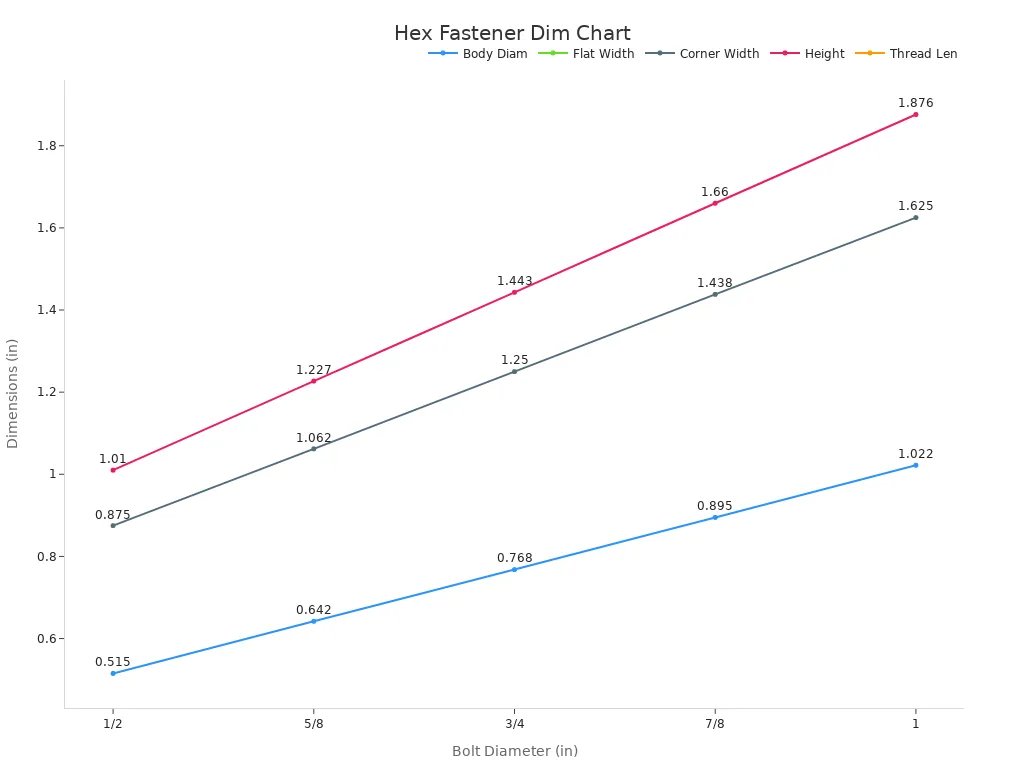
Measuring and Matching Hex Bolts and Nuts
Accurate measurements are crucial for matching hex bolts and nuts. Using the right tools ensures proper fit and prevents mechanical failures. Recommended tools include:
- Calipers: Measure the diameter, length, and head size with precision.
- Thread Gauge: Determine the thread pitch to ensure compatibility.
- Ruler or Tape Measure: Quickly measure the overall length of bolts.
Calibration of these tools is essential to maintain accuracy. Regularly calibrated tools reduce errors, ensuring the fasteners meet the required specifications.
Pro Tip: Always verify measurements before installation to avoid mismatched fasteners, which can compromise equipment safety.
Coatings and Finishes for Durability

Importance of Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance plays a vital role in extending the lifespan of fasteners used in construction equipment. Environmental factors such as moisture, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to chemicals can accelerate the degradation of fasteners. Corroded fasteners compromise the structural integrity of equipment, leading to potential failures and costly repairs. Selecting coatings that provide effective corrosion protection ensures that fasteners maintain their strength and functionality over time.
For instance, in outdoor environments, fasteners are often exposed to rain, humidity, and pollutants. Coatings act as a protective barrier, preventing oxidation and rust formation. This is particularly important for a hex bolt and nut, as these components are critical in holding heavy machinery and structures together. By prioritizing corrosion resistance, construction professionals can reduce maintenance needs and enhance equipment reliability.
Comparing Zinc Plating, Galvanization, and Other Coatings
Different coatings offer unique benefits and are suited for specific applications. The table below highlights the key features and applications of common coatings:
| Coating Type | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc Coatings | Sacrificial corrosion protection, excellent atmospheric resistance, cost-effective | Automotive, Construction, Heavy Equipment |
| Phosphate Coatings | Barrier against corrosion, enhances paint adhesion, moderate wear resistance | Components requiring further processing or finishing, where paint adhesion is critical |
Zinc coatings provide sacrificial protection, meaning they corrode in place of the fastener, thereby extending its lifespan. This makes them ideal for general construction and heavy equipment. Phosphate coatings, on the other hand, create a barrier against corrosion and improve paint adhesion, making them suitable for components that require additional finishing.
When comparing zinc plating and galvanization, performance metrics reveal significant differences in durability. Properly applied galvanized coatings can last over 50 years in rural areas and 20 to 50 years in industrial environments. Zinc plating, while cost-effective, may not perform well in harsh conditions such as marine environments, where high moisture and salt accelerate corrosion. Factors like coating thickness, environmental exposure, and maintenance practices also influence the longevity of these finishes.
Balancing Cost and Quality
Long-Term Benefits of High-Quality Fasteners
Investing in high-quality fasteners offers significant long-term advantages for construction equipment. Life cycle assessments (LCA) and cost analyses demonstrate that premium fasteners reduce maintenance and operational expenses over time. For example, fasteners used in insulating concrete forms (ICFs) contribute to lower energy costs and enhanced durability. While the initial cost of high-quality fasteners may seem higher, their ability to withstand wear and environmental stress minimizes the need for frequent replacements. This durability not only saves money but also reduces downtime, ensuring construction projects remain on schedule. Furthermore, the operational phase of construction equipment accounts for over 90% of its environmental impact. By choosing reliable materials, professionals can enhance sustainability while achieving cost efficiency.
Avoiding Low-Quality, Inexpensive Options
Low-cost fasteners often appear attractive due to their affordability, but they can lead to significant issues. These fasteners typically lack the strength and durability required for heavy-duty applications. Over time, they may corrode, loosen, or fail under stress, compromising the safety and functionality of construction equipment. Frequent replacements and repairs associated with low-quality fasteners increase overall costs and disrupt operations. Additionally, substandard materials can result in uneven load distribution, which accelerates wear on equipment components. Professionals should prioritize quality over cost to avoid these pitfalls and ensure the longevity of their machinery.
Cost-Effective Choices for Construction Equipment Longevity
Cost-effective solutions do not always mean choosing the cheapest option. Instead, they involve selecting materials and practices that balance affordability with performance. Market surveys highlight several strategies for achieving this balance:
- Equipment refurbishment extends the lifespan of machinery, reducing the need for new manufacturing.
- Upgrading older equipment improves energy efficiency and lowers fuel consumption.
- Recycling and proper disposal of materials promote waste management and sustainability.
- Responsible sourcing of fasteners ensures durability without compromising budget constraints.
By adopting these practices, construction professionals can enhance the longevity of their equipment while maintaining cost efficiency. Selecting the right hex bolt and nut, for instance, ensures reliable performance and reduces the likelihood of unexpected failures.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Preventing Mismatched Materials
Using mismatched materials for hex bolts and nuts can lead to premature wear, corrosion, or failure. Construction professionals must ensure material compatibility to maintain the integrity of fasteners. For example, pairing a stainless steel bolt with a carbon steel nut can cause galvanic corrosion, especially in humid or marine environments. This occurs when two dissimilar metals come into contact, creating an electrochemical reaction.
To prevent mismatches, professionals should:
- Match materials with similar corrosion resistance.
- Verify material grades and specifications before installation.
- Use manufacturer-recommended combinations for optimal performance.
Tip: Always consult material compatibility charts to avoid costly errors and ensure long-lasting connections.
Ensuring Proper Load Capacity
Improper load capacity selection is a common mistake that compromises safety and equipment performance. Hex bolts and nuts must withstand the forces exerted during operation without deforming or failing. Selecting fasteners with insufficient proof load or tensile strength can lead to catastrophic failures.
Professionals should:
- Calculate the maximum load requirements for the application.
- Refer to industry standards, such as ASTM or ISO, for load ratings.
- Choose fasteners with a safety margin to account for unexpected stresses.
Note: Overloading fasteners can cause thread stripping or bolt elongation, reducing the overall stability of the connection.
Accounting for Environmental Factors
Ignoring environmental conditions during fastener selection can result in corrosion, reduced strength, or mechanical failure. Construction sites often expose fasteners to moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations, which can degrade materials over time.
To address environmental factors:
- Use corrosion-resistant coatings, such as galvanization or zinc plating, in humid or wet conditions.
- Select stainless steel or alloy steel for high-temperature or chemically aggressive environments.
- Regularly inspect fasteners for signs of wear or corrosion.
Pro Tip: Consider the specific environmental challenges of the project site to ensure the fasteners maintain their performance and longevity.
Selecting the right hex bolt and nut is essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of construction equipment. Material, strength, size, coatings, and cost all play a critical role in determining the reliability of fasteners. High-quality fasteners not only enhance structural integrity but also reduce maintenance needs and operational downtime.
- The industrial fasteners market is projected to exceed USD 125 billion by 2029, reflecting their growing importance in construction and machinery.
- Experts recommend regular audits and maintenance of fasteners to ensure optimal performance and prevent unexpected failures.
By prioritizing quality and making informed choices, professionals can maximize equipment efficiency and minimize costly disruptions.
FAQ
What is the best material for hex bolts in outdoor construction?
Stainless steel is the best choice for outdoor construction. Its corrosion resistance ensures durability in humid or wet conditions. For cost-sensitive projects, carbon steel with protective coatings like galvanization can also perform well.
How can professionals ensure proper bolt and nut compatibility?
Professionals should match materials, thread pitch, and size specifications. Using tools like calipers and thread gauges ensures accurate measurements. Consulting manufacturer recommendations also helps avoid mismatches.
Why are coatings important for hex bolts and nuts?
Coatings protect fasteners from corrosion, extending their lifespan. Zinc plating, galvanization, and phosphate coatings provide varying levels of protection. The choice depends on environmental exposure and application requirements.
How often should fasteners be inspected?
Fasteners should be inspected regularly, especially in high-stress or corrosive environments. Monthly checks for signs of wear, corrosion, or loosening help maintain equipment safety and performance.
Are high-strength fasteners necessary for all construction applications?
High-strength fasteners are essential for heavy loads or extreme conditions, such as structural steel connections or heavy machinery. For lighter applications, standard-grade fasteners may suffice, provided they meet load requirements.
Post time: Apr-25-2025