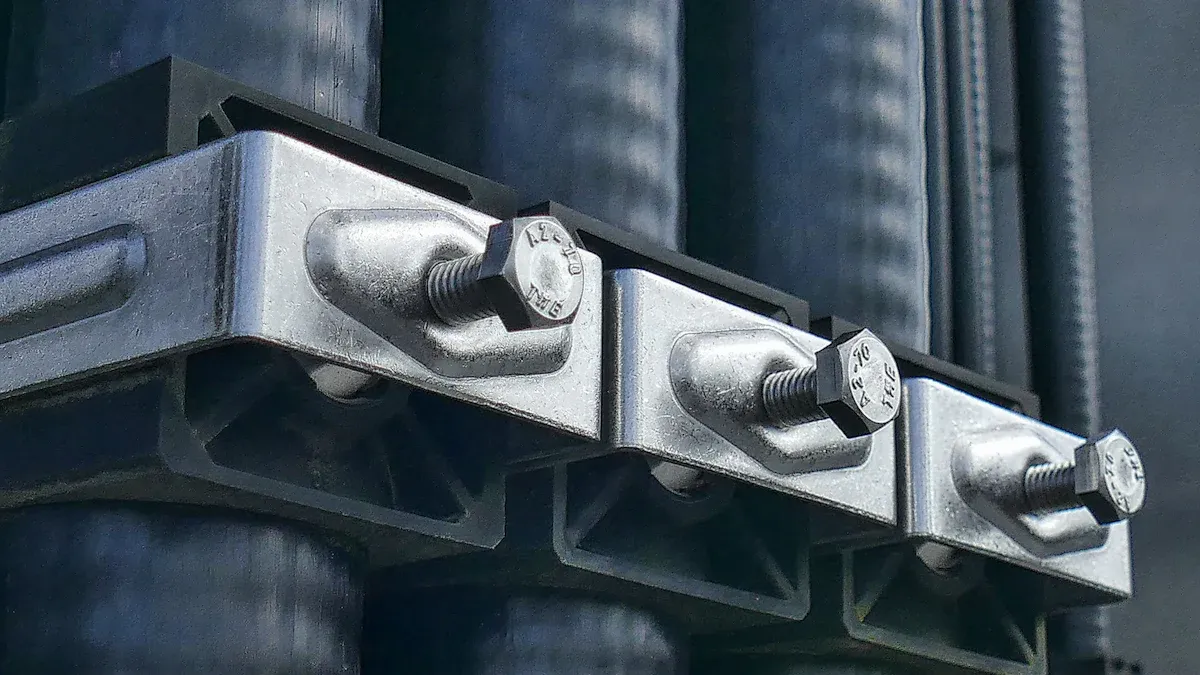

High-Strength Bolt Manufacturing uses advanced forging to increase material recovery rates from 31.3% to 80.3%, while tensile strength and hardness improve by nearly 50%.
| Process Type | Material Recovery Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Machined Input Shaft | 31.3 |
| Forged Input Shaft | 80.3 |
High-strength bolt products such as high-strength plow bolts, OEM track shoe bolts, and mine-grade section bolts support infrastructure and industrial growth worldwide.
Key Takeaways
- Advanced forging methods boost material use from 31% to over 80%, while increasing bolt strength and durability by nearly 50%.
- Careful raw material selection, precise forging, threading, heat treatment, and surface finishing ensure bolts meet strict quality and performance standards.
- Strict testing and quality control combined with proper packaging and export logistics guarantee reliable, traceable bolts for global infrastructure and industrial projects.
High-Strength Bolt Manufacturing Process

High-Strength Bolt Raw Material Selection
Manufacturers begin the process by selecting alloy steels and other materials that meet strict industry standards. The choice of raw material determines the final product’s strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. Engineers often specify low-phosphorus steels because phosphorus can cause embrittlement and increase the risk of fracture. Industry reports highlight the importance of dephosphoring, which removes phosphorus before heat treatment. This step prevents brittle fractures and improves mechanical properties, as confirmed by tensile strength and hardness testing. Companies like Ningbo Digtech (YH) Machinery Co.,Ltd. source high-quality steel to ensure every high-strength bolt meets the demands of critical infrastructure and industrial applications.
Note: Proper raw material selection forms the foundation for reliable, high-performance bolts.
| Process Stage | Description & Process Improvement |
|---|---|
| Raw Material Selection | Use of specific steels and alloys tailored to application requirements to ensure strength and durability. |
High-Strength Bolt Forging and Forming
Forging and forming shape the bolt and enhance its mechanical properties. Manufacturers use cold forging for small to medium bolts, which increases strength through strain hardening and delivers high precision. Hot forging suits larger bolts or harder materials, making them ideal for high-tensile applications. Advanced methods such as swaging and deep drawing refine the grain structure, improving strength and fatigue resistance. Engineering studies show that these techniques conserve material and increase strength without cutting, resulting in bolts with superior mechanical integrity.
- Swaging improves grain structure and overall strength.
- Deep drawing and hydroforming enhance fatigue resistance and stress distribution.
- These methods see use in industries like automotive, aerospace, and construction.
Ningbo Digtech (YH) Machinery Co.,Ltd. applies these advanced forging techniques to produce high-strength bolts that perform reliably under demanding conditions.
High-Strength Bolt Threading Methods
Threading gives bolts their fastening capability. Manufacturers use several methods, each with unique advantages. Thread rolling forms threads by deforming the material, which work-hardens the surface and produces stronger threads. This method is preferred for large production runs and standard thread sizes. CNC thread milling and grinding offer high precision and flexibility, making them suitable for custom or high-precision applications. CNC machines automate the process, reducing human error and ensuring consistent quality.
| Factor | CNC Machining | Traditional Forging/Manual |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | Very high, micrometer-level repeatability | Varies, depends on die wear or operator skill |
| Complexity of Shapes | Handles intricate geometries, custom features | Best for simpler shapes |
| Setup Cost | Medium (machine + programming) | Can be high for custom dies in forging |
| Production Speed | Slower for high-volume standard parts | Very fast if shapes are consistent (mass forging) |
| Flexibility | Extremely flexible; quick changeover | Low flexibility once dies are made |
| Material Utilization | Good, but can have more scrap than forging | Often very efficient in forging (less scrap) |
Tip: Thread rolling increases fatigue strength and improves surface finish, while thread cutting offers flexibility for special designs.
High-Strength Bolt Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is a critical step that enhances the bolt’s tensile strength, hardness, and ductility. Processes such as quenching, tempering, and annealing adjust the internal structure of the steel. Removing impurities like phosphorus before heat treatment is essential, as studies show that phosphorus segregation at grain boundaries can cause embrittlement and fracture under stress. Proper heat treatment ensures that each high-strength bolt can withstand high loads and harsh environments. Some advanced forming processes, such as those using twinning-induced plasticity (TWIP) steel, can eliminate the need for heat treatment, reducing production costs and lead times while still achieving excellent mechanical properties.
High-Strength Bolt Surface Finishing
Surface finishing protects bolts from corrosion and extends their service life. Manufacturers apply coatings such as zinc plating, galvanizing, or black oxide to create a barrier against moisture and chemicals. The choice of coating depends on the application and environmental conditions. Surface finishing also improves the bolt’s appearance and can enhance its performance in specific environments. Quality control at this stage includes checking coating thickness and adhesion to ensure long-term durability.
| Process Stage | Description & Process Improvement |
|---|---|
| Surface Coating | Various coatings (zinc plating, galvanizing, black oxide) improve corrosion resistance and durability. |
Ningbo Digtech (YH) Machinery Co.,Ltd. uses advanced surface finishing technologies to deliver high-strength bolts that meet international standards for corrosion resistance and durability.
High-Strength Bolt Quality Assurance and Global Export

High-Strength Bolt Quality Control and Testing
Manufacturers rely on strict quality control to ensure every high-strength bolt meets international standards. They use advanced metallurgy and precision engineering to improve bolt strength and durability. Digital inspection methods and automated quality control systems allow real-time checks, which help reduce defects and maintain product integrity. Companies like Sinorock set an example by managing suppliers, inspecting incoming materials, and verifying outgoing products. Their annual Quality Month encourages employees to focus on continuous improvement and quality awareness.
Adhering to standards such as ASME B18.2.1, ISO, and ASTM ensures that each high-strength bolt meets strict dimensional, material, and mechanical requirements. This builds trust with global buyers and helps manufacturers overcome challenges from different international regulations.
Manufacturers use a range of tests and certifications to prove bolt reliability. These include:
- Magnetic Particle Inspection to find surface cracks.
- Profile Projector for micron-level dimension checks.
- Roughness Tester to measure surface finish.
- Coat Meter to check coating thickness for corrosion resistance.
- Mechanical tests like tensile, proof load, shear, and prevailing torque.
- Metallurgical tests for microstructure and decarburisation.
- Certifications such as ISO 9001:2015 and UKAS accreditation.
A comprehensive testing approach includes initial appearance inspection, dimension checks, chemical composition analysis, tensile strength testing, and corrosion resistance testing. These steps have led to a significant drop in fastener failure rates.
| Test Type | Description | Standards / Certifications |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength Testing | Measures ultimate tensile strength, yield strength, elongation on bolts of various sizes | BS EN ISO 3506-1, BS EN ISO 898-1 |
| Proof Load Testing | Verifies bolt can withstand specified proof load without permanent deformation | BS EN ISO 3506-1 |
| Shear Testing | Assesses bolt resistance to shear forces | ASTM A193, ASTM A194 |
| Prevailing Torque Testing | Measures resistance to loosening under vibration and stress | ISO 2320, BS 4929 |
| Hardness Testing | Surface and core hardness testing to ensure material strength | ASTM A194 |
| Chemical Composition | Spark-OES, ICP-OES analysis to verify material makeup | UKAS accredited methods |
| Metallurgical Testing | Microstructure, decarburisation, phase analysis, metal cleanliness | UKAS accredited methods |
| Corrosion Resistance | Salt spray and humidity testing to evaluate surface treatment durability | Industry-specific standards |
| Certifications | ISO 9001:2015, UKAS accreditation to ISO/IEC 17025:2017, Nadcap for aerospace quality systems | International and industry-recognized accreditations |
These tests and certifications provide measurable proof that high-strength bolts are reliable and ready for critical applications in aerospace, nuclear, marine, and construction projects.
High-Strength Bolt Packaging and Export Logistics
After passing all quality checks, manufacturers prepare high-strength bolts for global export. Proper packaging protects bolts from damage during shipping and storage. Companies use sturdy cartons, wooden crates, or steel drums, depending on the size and weight of the shipment. Each package receives clear labeling with product details, batch numbers, and compliance marks.
Careful packaging and labeling help customs officials and buyers verify product authenticity and traceability.
Export logistics teams coordinate with international freight carriers to ensure timely delivery. They manage customs documentation, certificates of origin, and export licenses. Many manufacturers use digital tracking systems, which allow buyers to monitor shipments in real time. Integration of IoT and predictive maintenance in production supports consistent quality, making sure every high-strength bolt shipment meets the requirements of global customers.
Manufacturers who follow these steps maintain a strong reputation in the global market. Their commitment to quality assurance and reliable logistics ensures that high-strength bolts arrive safely and perform as expected in demanding environments.
Every stage in high-strength bolt manufacturing, from forging to export, supports safety and performance. The Fastener Quality Act and international standards like ISO 898-1 and ASTM F568M ensure strict quality control. Buyers and engineers trust these processes to deliver reliable high-strength bolt solutions for critical projects.
FAQ
What industries use high-strength bolts?
High-strength bolts support construction, automotive, energy, and infrastructure projects. These bolts provide reliable connections in bridges, buildings, heavy machinery, and wind turbines.
How do manufacturers ensure bolt quality?
Manufacturers use strict testing, including tensile, hardness, and corrosion checks. They follow ISO and ASTM standards. Digital inspections help maintain consistent quality.
What packaging protects bolts during export?
- Sturdy cartons
- Wooden crates
- Steel drums
Each package includes clear labels, batch numbers, and compliance marks for safe, traceable delivery.
Post time: Jul-09-2025